In this article we are discussing renewable energy, what is renewable energy, and sources of renewable energy. We will also discuss what is renewable energy sources or renewable resources and the benefits or advantages of renewable energy.

What is renewable energy
·
Renewable energy is the
type of energy that is produced using natural resources that are constantly
replaced and never run out.
·
Renewable energy is energy that is collected from sources or processes that are naturally and constantly replenished,
regenerated, or replaced. The sources include sunlight, wind, the movement of water (hydroelectric and tidal), geothermal heat, and biomass.
Renewable energy sources are such sources that
are plentiful and all around us.
Although
renewable energy is considered a solution for the future of our power needs,
we have been harnessing and consuming the natural power of nature for
centuries.
Renewable energy is an alternative to Fossil
fuels (coal, oil, and gas). These fossil fuels are non-renewable resources, they
take hundreds of millions of years to form. Fossil fuels cause emissions of harmful
greenhouse gases, such as carbon dioxide when they are burnt to produce energy.
While consumption of renewable energy creates
far lower emissions than burning fossil fuels. Transitioning from fossil
fuels to renewable energy is definitely the key to addressing the climate
crisis.
Renewables are now considered cheaper in
most countries, and they generate three times more jobs than fossil fuels.
Renewable Energy Stats
According to the stats, from 2011 to 2021, renewable energy has grown from 20% to 28%
of the global electricity supply. Fossil energy decreased from 68% to 62%, and
nuclear from 12% to 10%. The hydropower’s share decreased from 16% to 15%
while power from sun and wind increased from 2% to 10%. Biomass and geothermal
energy have grown from 2% to 3%. More than 3000 gigawatts are installed in 135
countries, while 156 countries plan to fulfill their energy needs from the renewable energy sector.
Renewable Energy in Europe
According to Eurostat in 2019,
renewable energy sources made up 34% of gross electricity consumption in the
EU, slightly up from 32% in 2018.
.jpg)
Wind and hydropower contributed about
two-thirds of the total electricity generated from renewable sources (about 35%
each). The remaining electricity generated was from solar power (13%), solid
biofuels (8%), and other renewable sources (9%). Solar power is the source that
is growing fast: in 2008, it accounted for 1%.
Where is Renewable Energy Used the Most?
Germany
is the country that uses the highest amount of renewable energy with 12.74%.
This was followed by the UK at about (11.95%), Sweden at (10.96%), Spain at (10.17%), Italy at (8.8%), Brazil at (7.35%), Japan at (5.3%), Turkey at (5.25%), Australia at (4.75%) and the
USA at (4.32%) all making up the top ten.
Renewable Energy in the United States
Renewable energy generates
electricity about 20% of all the U.S.,
and that percentage is growing continuously. The total electricity production
in 2021 among the types of renewable power is graphically shown below:

In
2022, solar and wind are considering adding more than 60% of
the utility-scale generating capacity to the U.S. (46% from solar,
17% from wind).
The United States has rich renewable energy resources. Its potential to generate renewable energy is about 100 times that
of the nation’s annual electricity need.
Importance of Renewable Energy
Renewable energy sources are resources
that can be used multiple times.
Renewable resources are considered particularly important
because they can replace non-renewable or finite resources in
energy production. In addition, renewable resources can provide cleaner energy
solutions than non-renewable resources such as coal and fossil fuels.
Other examples of renewable resources include wind energy,
hydroelectric power, and geothermal energy. Wind turbines convert the kinetic
energy of the wind into electricity, while hydroelectric plants collect water
in reservoirs and release it to spin turbines. Geothermal power plants use the
heat generated by the mantle to generate steam that drives turbines.
Renewable energy offers many advantages, including an
available source of energy production. As the industry grows, jobs are created
in the design and installation of future renewable energy solutions. Renewable
resources also provide developing countries with better access to energy and
can also reduce energy costs.
Renewable energy is energy that
comes from natural sources that can be regenerated or replaced.
Renewable energy is energy derived from the earth's natural
resources that are not finite or depletable, such as B. wind and sunlight.
Renewable energy is an alternative to conventional energy sources based on
fossil fuels and is generally much less harmful to the environment.
Renewable energy is the energy obtained from natural processes
that are replenished at or faster than the rate at which it is consumed. There
are many forms of renewable energy, either directly or indirectly from the sun
or heat generated deep inside the earth. This includes energy from solar, wind,
geothermal, hydroelectric, and marine sources, solid biomass, biogas, and liquid
biofuels. However, biomass is a renewable resource only if its consumption rate
does not exceed its regeneration rate.
Renewable energy means sustainable energy - energy like the
sun that won't run out or be inexhaustible. This means that energy can replace
the most commonly used unsustainable energy sources - such as coal.
Sources of Renewable Energy
There
is a range of renewable sources that have been developed, with each offering its
own advantages and challenges depending on factors such as geographical
location, requirements for use, and even the time of year.
All these renewable energy sources are
plentiful and all around us.
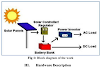
1. Solar
The
sun is the most potent source to supply our power needs because the sun supplies energy to the earth in just one hour is enough to fulfill the planet’s power needs for an entire year. However, the challenge is how to harness and use this vast potential.
We currently use solar energy
to heat buildings, warm water, and power our devices. The power from the sun is
collected using solar or photovoltaic (PV) cells, which are made from silicon
or other materials. These cells transform sunlight into electricity which is DC and can
power anything from the smallest garden light to entire neighborhoods. These
solar cells form a panel and the combination of panels is mostly installed on
the rooftop of a house and power it. While Solar farms can also be created to
supply the community or colony.
Solar-powered energy
systems are clean, pollutants-free energy sources and they don't produce
greenhouse gases or carbon.
2. Wind
In
this type of renewable energy, the energy is obtained from the wind. Its process is
just like old-fashioned windmills. The blades are installed freely to rotate with
the wind. The difference is, that the windmill uses the power of the wind to rotate
the millstones, whereas, in the latest wind power system, turbines are rotated by
blades to generate electricity.
Wind turbines are installed
on such sites where wind pressure is high. These sites include hilltops,
plains, and open fields.
3. Hydroelectric
Hydroelectric
power works like wind power. The difference is that it uses moving water to
spin the turbine of the generator to produce electricity. In hydropower, the
turbine of the generator is either rotated by fast-moving water in rivers or
from waterfalls. In most countries, energy needs are widely fulfilled by hydroelectric
power. It is currently the largest renewable energy source in the United
States, most Asian countries, and all over the world.
Hydroelectric dams are
built which is a renewable energy source. However, the construction of the
larger ‘mega-dams’ divert natural water sources and they also create a negative
impact on animal and human populations due to restricted access to the water
source. If carefully managed, smaller hydroelectric power plants (under 40
megawatts) do not have such negative effects on the local environment.
4. Biomass
Biomass
energy is obtained from the organic material of plants and animals, including
crops, trees, and waste wood. This biomass is burned to create heat, which is
used to power a steam turbine and generate electricity.
Biomass
has some negative impact on the environment because it produces which causes pollution.
Studies have shown that biomass from forests can produce higher carbon
emissions than fossil fuels, and it also hurts biodiversity.
If it is managed well, its diverse effect can be decreased.
5. Geothermal
Geothermal
energy is obtained from the heat trapped in the Earth’s core which is
created by the slow decay of radioactive particles in rocks at the center of
the planet. For this purpose, deep wells are drilled to bring highly heated water
to the surface and that water is then used as a hydrothermal source to rotate
turbines, and electricity is produced. To make this renewable resource greener,
the hot water and steam can be pumped back to earth to lower emissions to the
possible level.
Geothermal energy is mostly
available in geographical locations like Iceland with a rich and ready supply
of geothermal resources.
6. Tidal
In
this type of renewable energy, the energy is obtained from the tides of the
sea. The tide is generated by the constant gravitational pull of the moon. For this
purpose, tank-like structures are constructed on the sea sides or beach, and the
water from the tide enters the tank through a hole. The turbine or generator
is placed there in the hole, which rotates by entering and outing water to
the tank and back to sea. The power generated by the tide may not be constant,
but it is reliable, making this a relatively new resource of renewable energy.
Benefits of Renewable
Energy
The advantages and
benefits of renewable energy are numerous and affect the economy, environment,
national security, and human health. Here are some of the benefits and
advantages of using renewable energy:
· It enhances the reliability, security, and resilience of the nation’s power grid
· It
increases job creation throughout renewable energy industries
· It
reduces carbon emissions and air pollution from energy production
· It
increases the energy independence of a nation
· Renewable
energy increases affordability, as many types of renewable energy are
cost-competitive with traditional energy sources
· It
expands clean energy access for non-grid-connected or remote, coastal, or
islanded communities
· Renewable
energy is environment friendly and it is mostly free from all types of
pollution.




0 Comments